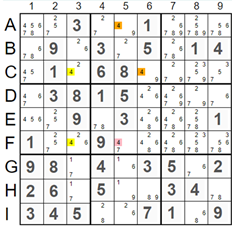
The picture on the left illustrates another example of the Rectangle Elimination technique. The pattern is formed by candidate 4 in rows C and F and columns 3 and 5. If cell F5 has a value of 4, then candidate 4 in cell F3 should be removed. There is a strong link between the two candidate 4 in column 3. When 4 is removed from cell F3, this value should be assigned to cell C3. Therefore, if we have a value of 4 in cells F5 and C3, all other candidate 4s should be removed from rows C and F and columns 3 and 5. In this case, the value 4 does not exist in the top middle square, rendering the sudoku puzzle invalid. Our assumption that cell F5 has a value of 4 is incorrect, and we can remove candidate
'4' marked red from this cell.